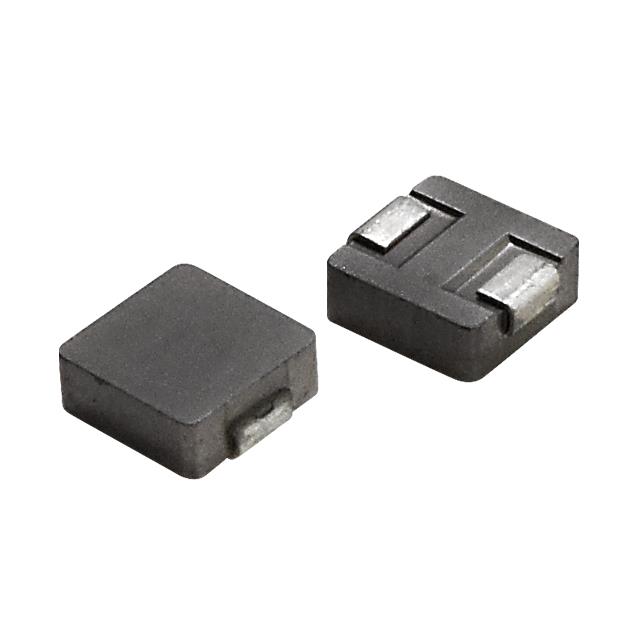
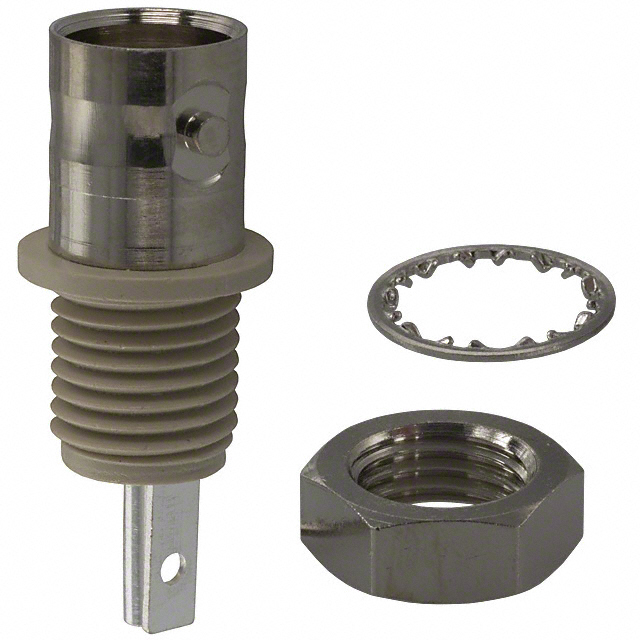
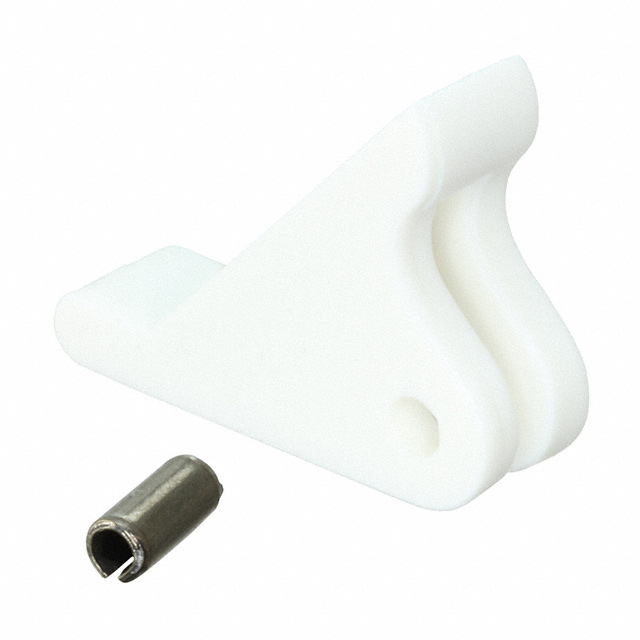
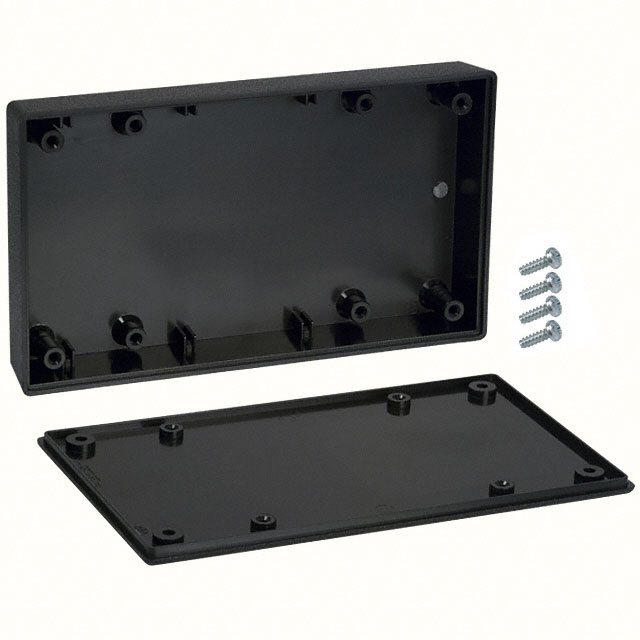
31-10
CONN BNC RCPT STR 50 OHM SOLDER

83-1T
CONN ADAPT PLUG-JACK UHF

11-140
CONN BARRIER STRP 11CIRC 0.375"

7-141
CONN BARRIER STRIP 7CIRC 0.438"

Y-141
CONN TERM BLK Y-SOLDER BARRIER

3-142
CONN BARRIER STRIP 3CIRC 0.563"

10-142
CONN BARRIER STRP 10CIRC 0.563"

8644
EJECTOR CARD LEVEL ACTION